Whether you’re a medical professional or a bystander, it’s important to know what to do in the event of major blood loss. Accidents happen and rapid treatment is key. If you’re equipped with knowledge of first aid and an understanding of the different types of bleeding, you’ll be better poised to intervene and help save the victim.
Differentiating Between the Types of Bleeding
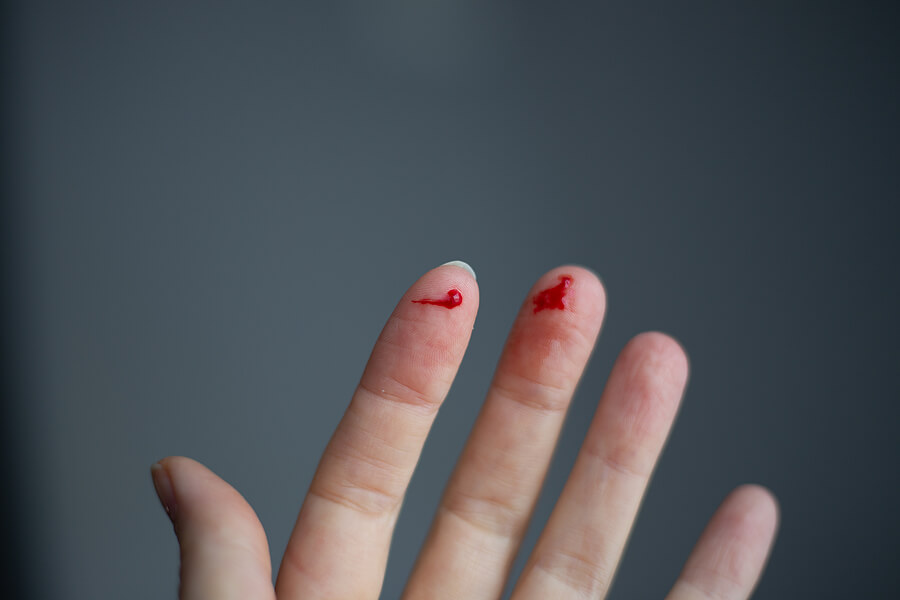
It’s helpful to know how to tell the difference between the types of bleeding. Recognizing the type of bleeding can help you determine what the best treatment is and whether medical attention is necessary.
Consider the following characteristics of the types of external bleeding:
- Arterial bleeding: This type of bleeding is characterized by a spurting or pulsing movement caused by the heart. Because the blood is coming directly from an artery, it tends to be a bright red color.
- Venous bleeding: Bleeding from a major vein injury tends to ooze instead of spurt. Blood from venous bleeding can also be darker in color than other types of bleeding because the blood does not carry as much oxygen.
- Capillary bleeding: This type of bleeding is, in general, less severe than the other two. Like venous bleeding, capillary bleeding will ooze from the skin, but it is superficial and will appear milder.
Recognizing Signs and Symptoms of Bleeding
In most cases, it’s easy to spot external bleeding. Severe bleeding will be obvious right away. Depending on the type of bleeding, you may notice blood spurting or flowing from the injury site. If you suspect that you may have been injured, check your clothes and skin for blood or stains.
Internal bleeding can be a little more difficult to spot. If the bleeding is minor, symptoms may include small red marks on the skin or slight bruising. Major bleeding can result in a range of symptoms like nausea, headache, or blood in the urine.
Immediate First Aid for Bleeding
If you or someone else is bleeding, it’s important to take action and stop the bleeding quickly. First, locate the source of the bleeding and assess the level of severity.
Minor cuts and wounds can be treated with regular bandages. Be sure to monitor the injury to make sure that the bleeding stops. If the bleeding does not stop or if it seems like the wound might be infected, seek medical treatment right away.
If the bleeding is life-threatening, you should first call 911. The operator will likely provide some guidance for what action to take depending on the situation. You should try to cover the wound and apply pressure. If there is a first aid kit accessible, use bandages. If not, you can use cloth such as a nearby shirt. Bleeding leg and arm wounds should be treated with a tourniquet, while other areas should be bandaged and secured with roller gauze.
Treating Severe Bleeding: Techniques and Considerations
The most effective bleeding treatment can vary based on the type of bleeding. For example, light capillary bleeding can sometimes stop on its own. Bandages can help if the bleeding is more severe, but minor capillary bleeding does not require significant treatment.
Arterial bleeding, however, always requires immediate response. Because this type of bleeding is caused by a major artery, treatment is more intense. If you’re treating a patient with arterial bleeding, you’ll need to apply direct pressure right away.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Bleeding can be a severe medical issue and should be taken seriously. Hemorrhage caused by a traumatic injury is the leading cause of death in the U.S. for people under the age of 46. No matter which type of bleeding it is, major bleeding should be treated by a medical professional.
You should seek medical attention in the following cases:
- The bleeding is severe.
- The bleeding will not stop.
- You suspect internal bleeding.
- You feel lightheaded or faint.
When in doubt, it’s a good idea to get medical help in the event of severe bleeding. Bleeding emergencies can become serious quickly.
Preventing and Minimizing Bleeding Risks
As always, it’s important to be careful and prevent injury in the first place. Be sure to exercise caution in situations that could cause injury like cooking or operating tools. Wear appropriate safety gear when handling sharp objects such as knives, tools, or glass.
Another way to prepare is by gathering first aid items for your home and car. Make sure the first aid kit is well-stocked with bleeding treatment items such as Band-Aids, gauze, and bandages. You should also keep several pairs of disposable gloves to use when treating bleeding. Trauma Packs are ideal for your house or car in case of a large scale bleed or a shooting. Additionally, taking first aid training not only equips you with the knowledge and skills needed to provide immediate medical assistance in emergencies but also ensures you can effectively utilize these supplies when the need arises.
FAQs
The three types of external bleeding are capillary bleeding, venous bleeding, and arterial bleeding.
If you or someone else is experiencing severe bleeding, you should call 911. Severe bleeding requires medical treatment right away. In the meantime, apply pressure to the wound and cover it with bandages or cloth.
You should seek medical attention if the bleeding is severe (for example, if it soaks through bandages quickly) or if it does not stop. You should also seek medical help if you suspect internal bleeding.
The type of bleeding is determined by the site of the bleeding. Capillary bleeding comes from the skin capillaries, while venous comes from a vein and arterial comes from an artery. There are also differences between the bleeding––such as spurting versus flowing––and blood itself, such as color.
Ready to learn more about first aid? Take a Basic First Aid course with SureFire CPR, Southern California’s top training program. You’ll gain hands-on experience and learn from industry experts.