Occasionally, children complain that their “chest hurts”. Of course, with an adult, one would automatically assume “chest pain” signifies heart problems. But is this the case with children’s complaints of chest discomfort?
Fortunately, children typically do not have cardiac related chest pain. There will always be the exception and when cardiac involvement is suspected, a 9-1-1 call is appropriate activating the Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS) protocols and possibly saving the child’s life.
What Is PALS?
PALS is a certification designed for medical personnel who deal with life-threatening situations that involve children. Many hospitals and medical institutions require staff members to become PALS-certified to ensure medical personnel can provide crucial support in adolescent emergencies.
Typically, PALS training offers a viable certification for many medical professionals, including:
- Doctors
- Firefighters
- First responders
- Nurses
- Paramedics
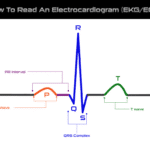
It also is important to note that most everyday citizens do not receive PALS training. In fact, PALS training programs account for the fact that only medical professionals will have access to certain drug and electrocardiogram (ECG) machines that can be used to administer life-saving assistance in pediatric emergencies.
What Does a PALS Training Program Include?
A PALS training program teaches medical personnel about a broad assortment of pediatric emergency response techniques. The program offers insights into the application of various life-saving techniques in situations where a child’s life is threatened by a medical emergency. That way, medical personnel will learn about pediatric cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) and other techniques that they can use to deal with many potential pediatric dangers.
Furthermore, a PALS certification class emphasizes the following topics:
- The systematic approach to pediatric assessment
- PALS pharmacology terms and definitions
- Airway management
- The importance of vascular access (including intraosseous training)
- Management of pediatric respiratory emergencies
- Basic life support (BLS) overview
- How a medical professional can serve as a leader in a pediatric resuscitation team
A PALS certification class usually features a combination of hands-on and classroom lessons to teach medical personnel about pediatric life-saving techniques. It also may include numerous pediatric case studies and simulations.
PALS certification will stay active for two years. Enrollment in a PALS initial class is essential for medical professionals who need to obtain PALS certification for the first time. Comparatively, medical personnel who need to renew their PALS certification can participate in a PALS update or renewal class.
Why Is PALS Training Essential for Pediatric Emergencies?
With PALS training, medical personnel are equipped to handle pediatric emergencies any time they occur.
A comprehensive PALS training program offers many benefits, including:
- In-Depth Lessons: A PALS class provides medical personnel with extensive insights into pediatric emergencies. As a result, medical professionals can gain the skills and know-how needed to stay calm, cool and collected in a wide range of life-threatening scenarios.
- Experienced Teachers: In many instances, a PALS class is taught by a medical professional who possesses real world experience. This instructor can respond to students’ PALS concerns and questions and ensure they understand how to deliver crucial support in adolescent emergencies.
- Immediate Certification: A PALS class can take between 6 – 12 hours to complete. Plus, a student usually can receive a PALS certification card the same day that he or she finishes a PALS training program.
In addition, PALS training ensures medical personnel understand how to assist children who suffer chest pain. A PALS class even teaches medical professionals how to identify and mitigate chest pain symptoms quickly.
What Should You Do If Your Child Experiences Chest Pain?
Should your child complain of pain to his chest, you can breathe easy knowing the cause will most likely be benign in origin. Common causes identified by Cincinnati’s Children’s Hospital are among the following:
- Costochondritis: inflammation that occurs within the “joint” between the rib and breastbone. This symptom is caused with upper respiratory viral illness or frequent coughing and is usually treated with anti-inflammatory medications such as ibuprofen.
- Injury: impact (which can be serious) or strain with frequent coughing, contact sports or falls can create discomfort to the chest. Treatment depends on the extent of the injury that is minor in nature is generally supportive in nature with rest and over-the-counter pain medications. All injuries to the chest should be evaluated by a physician particularly when difficulty breathing is associated.
- Stress and Anxiety: a condition typically associated with adults, children can also suffer from the side effects of perceived stress or worry. Determining the cause of this type of discomfort aides in recognizing possible interventions for treatment.
- Precordial Catch Syndrome: a rare condition that typically affects adolescents in which a sudden onset of sharp pain associated with inspiration occurs along the chest or back. This condition has no significant side effects and generally resolves itself within moments. (information obtained the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital website: www.cincinnatichildrens.org)
Parents can breathe easy knowing chest pain occurring in children is rarely cardiac in origin. However, a few rare circumstances may indicate heart involvement in children. Those will be reviewed in part-two of this article, posted tomorrow on this site.