An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a powerful tool that allows medical professionals to assess heart health by recording the electrical activity of the heart. What might seem like a collection of lines and waves on a piece of paper is, in fact, a highly detailed account of the heart’s rhythm, electrical impulses, and overall function. Learning how to read an ECG can be a valuable skill for healthcare professionals and those interested in heart health.
What is an Electrocardiogram (EKG/ECG)?
An ECG (also called EKG) is a diagnostic tool used to monitor the electrical impulses of the heart. It’s often used by doctors, nurses, paramedics, and healthcare professionals to detect heart abnormalities, monitor heart rhythms, and diagnose various cardiovascular diseases.
An ECG records the heart’s electrical signals in the form of waves and intervals, providing important data that helps clinicians understand the health of the heart muscle and its rhythm. This detailed, graph-like printout helps doctors quickly spot irregularities that might indicate heart problems such as arrhythmias, heart attacks, or even electrolyte imbalances.
The Basics of an ECG
Acute coronary syndromes (ACS) are conditions related to a sudden decline in blood flow to the heart. Conditions might include:
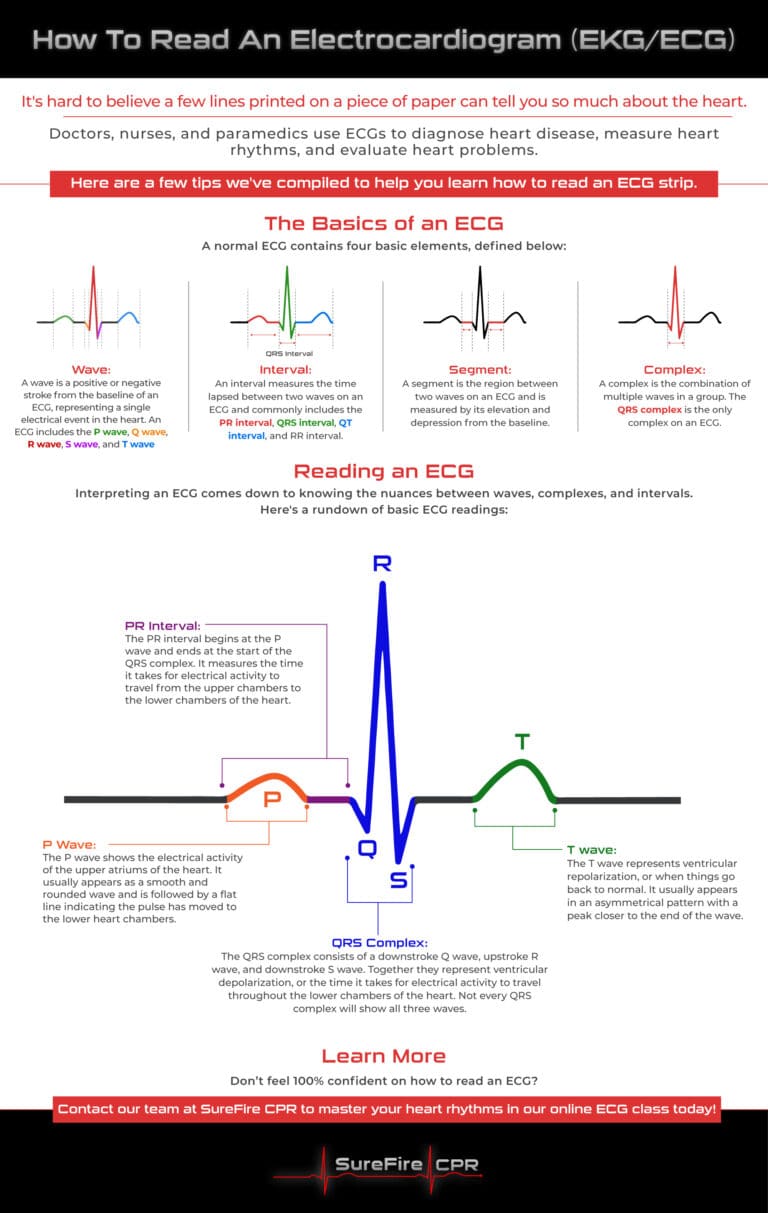
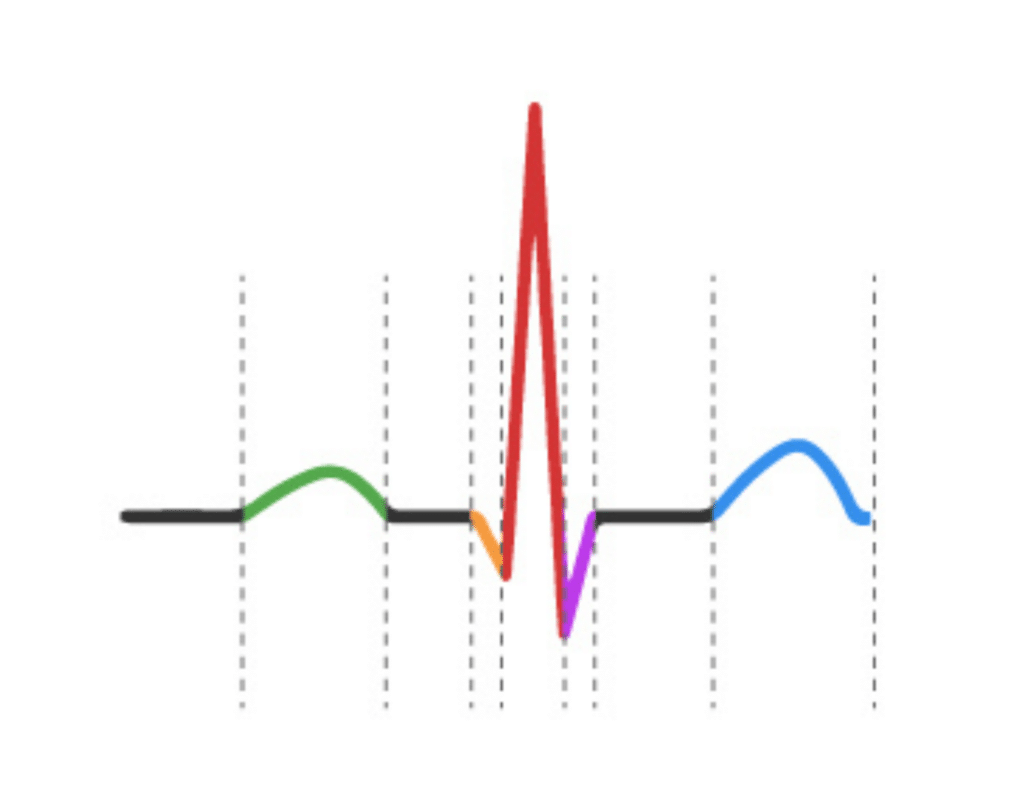
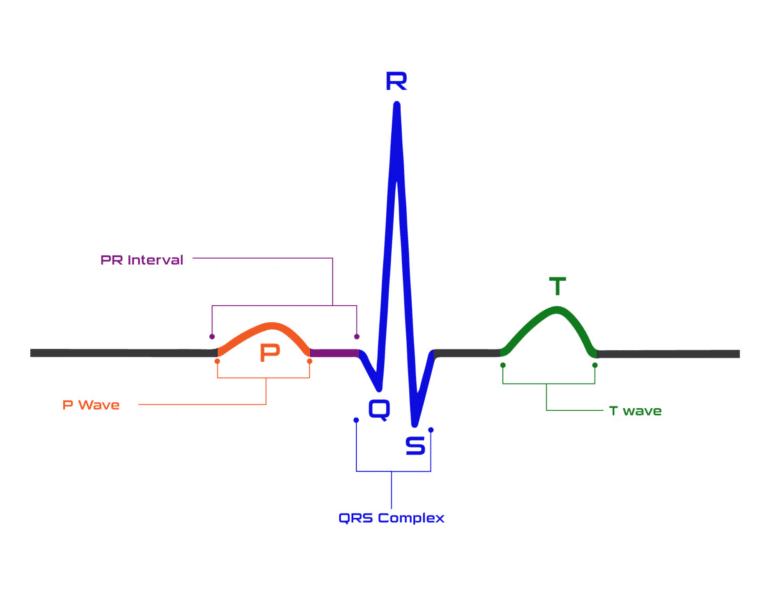
Waves
A wave is a positive or negative stroke that represents a single electrical event in the heart. There are five primary waves in a standard ECG:
- P Wave: Represents the electrical activity in the atria (upper chambers of the heart).
- Q Wave: A downward deflection of the wave.
- R Wave: The first upward deflection of the wave.
- S Wave: A downward deflection following the R wave.
- T Wave: Represents the repolarization (recovery) of the ventricles (lower chambers of the heart).
Intervals
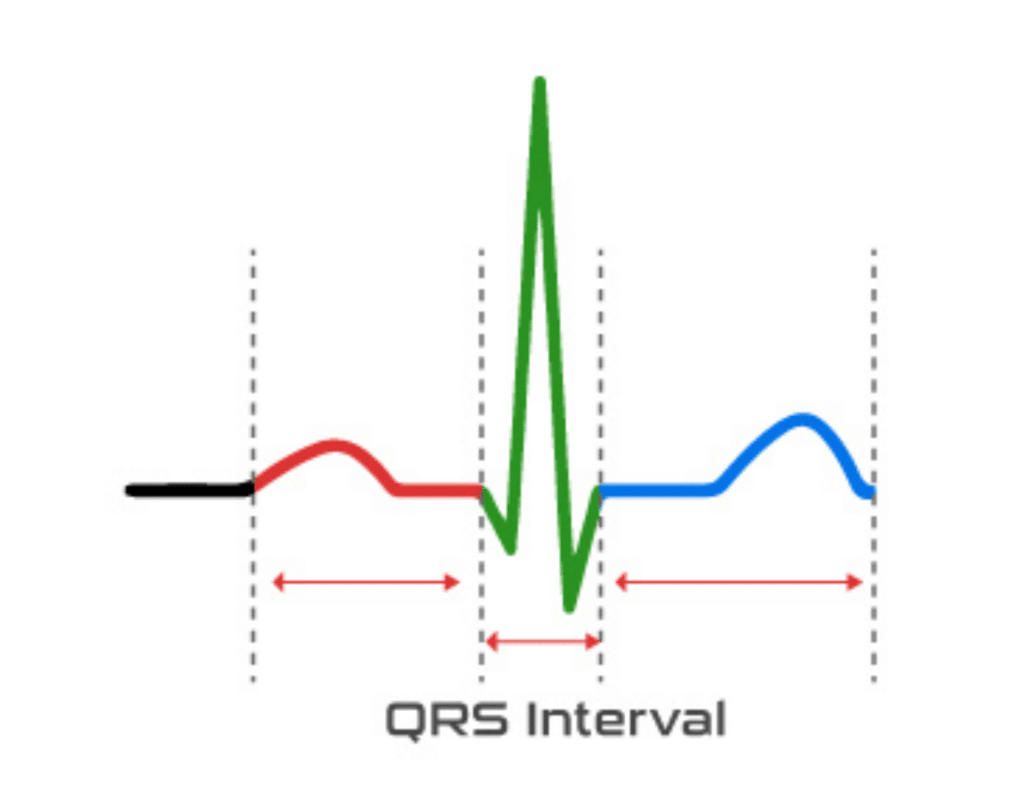
An interval measures the time between two waves on an ECG. Common intervals include:
- PR Interval: Time taken for the electrical impulse to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
- QRS Interval: Time it takes for the electrical impulse to travel through the ventricles.
- QT Interval: Time from the start of ventricular depolarization to the end of ventricular repolarization.
- RR Interval: Time between two successive R waves (measuring heart rate).
Segments
A segment is the region between two waves and is measured based on its elevation or depression from the baseline. Segments give information on how well the heart muscle is conducting electricity.

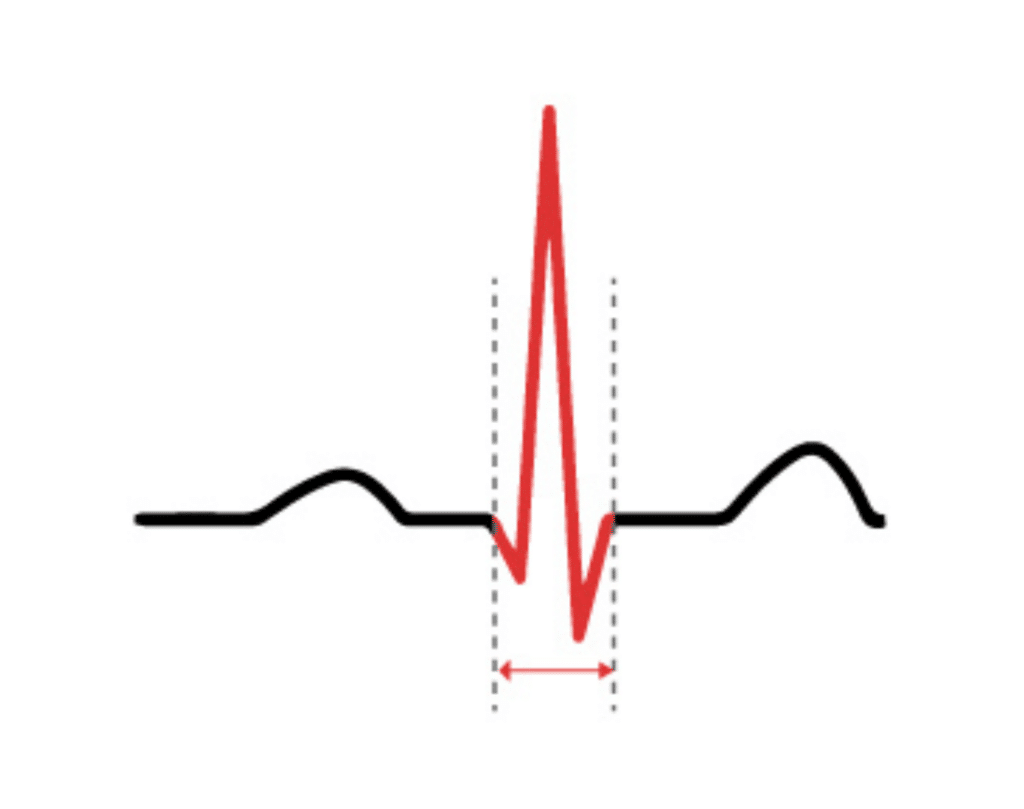
Complex
A complex is a group of multiple waves that form a single unit. The QRS Complex is the most significant complex in an ECG. It represents the electrical activity during ventricular depolarization.
Reading an ECG
Now that we’ve covered the basics, let’s dive into how to read an ECG strip. When you look at an ECG, you’re essentially interpreting the rhythm and electrical events of the heart. Let’s explore some of the most important readings you’ll encounter:
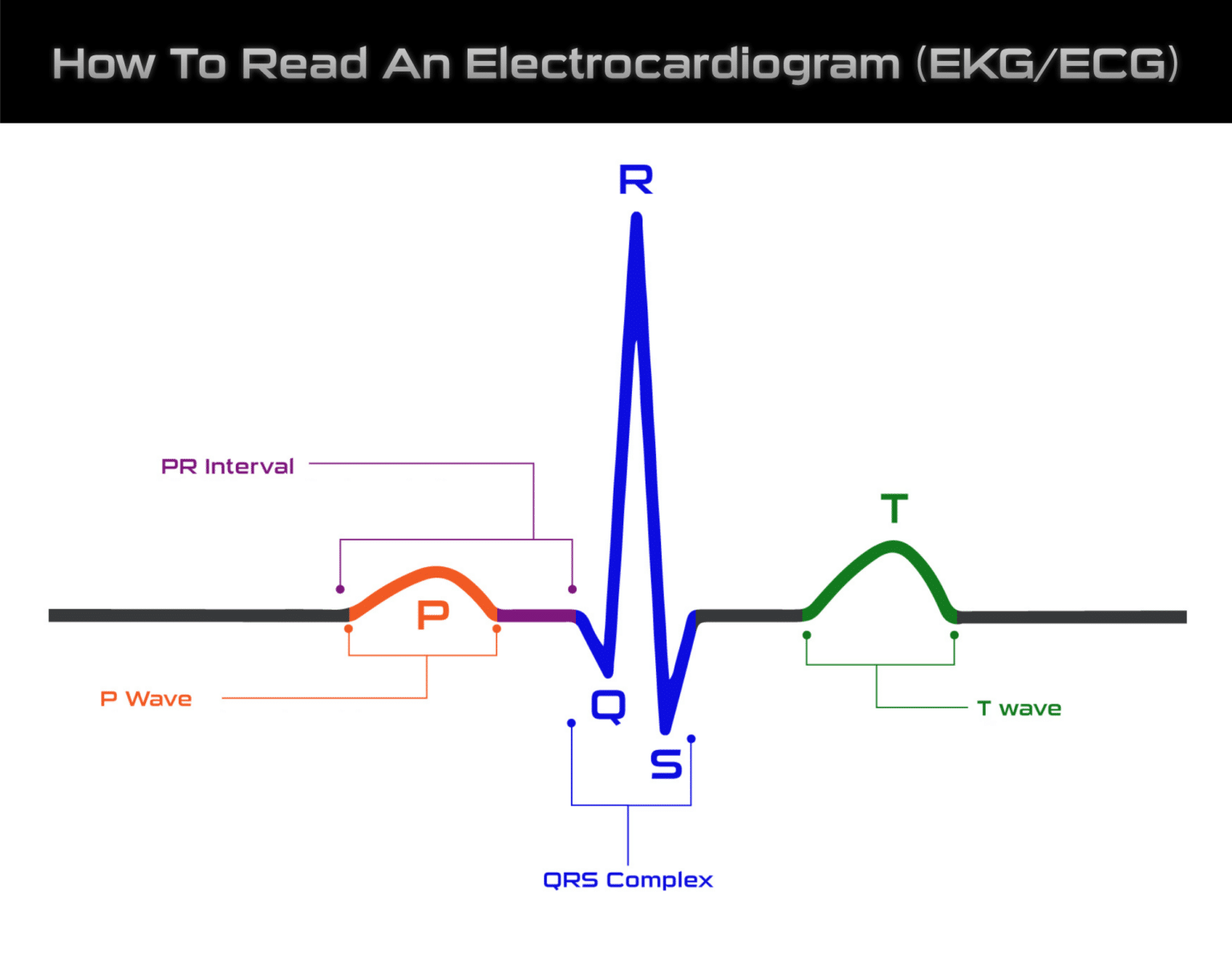
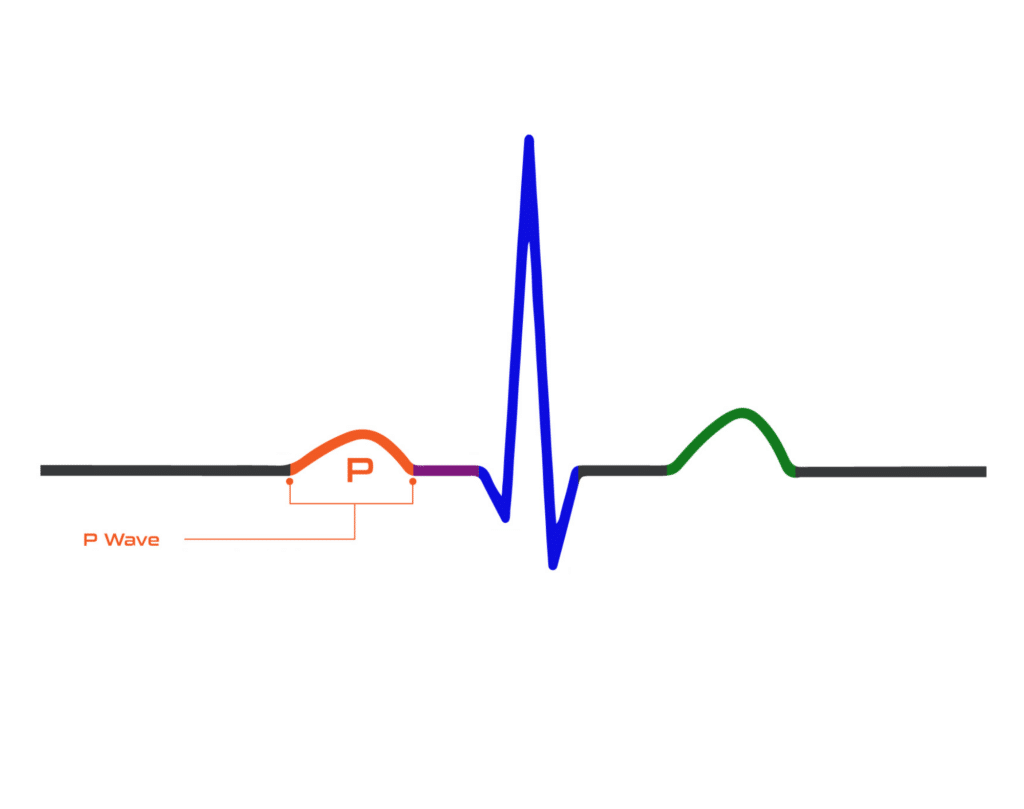
P Wave
The P wave shows the electrical activity of the upper atriums of the heart. It usually appears as a smooth and rounded wave and is followed by a flat line indicating the pulse has moved to the lower heart chambers.
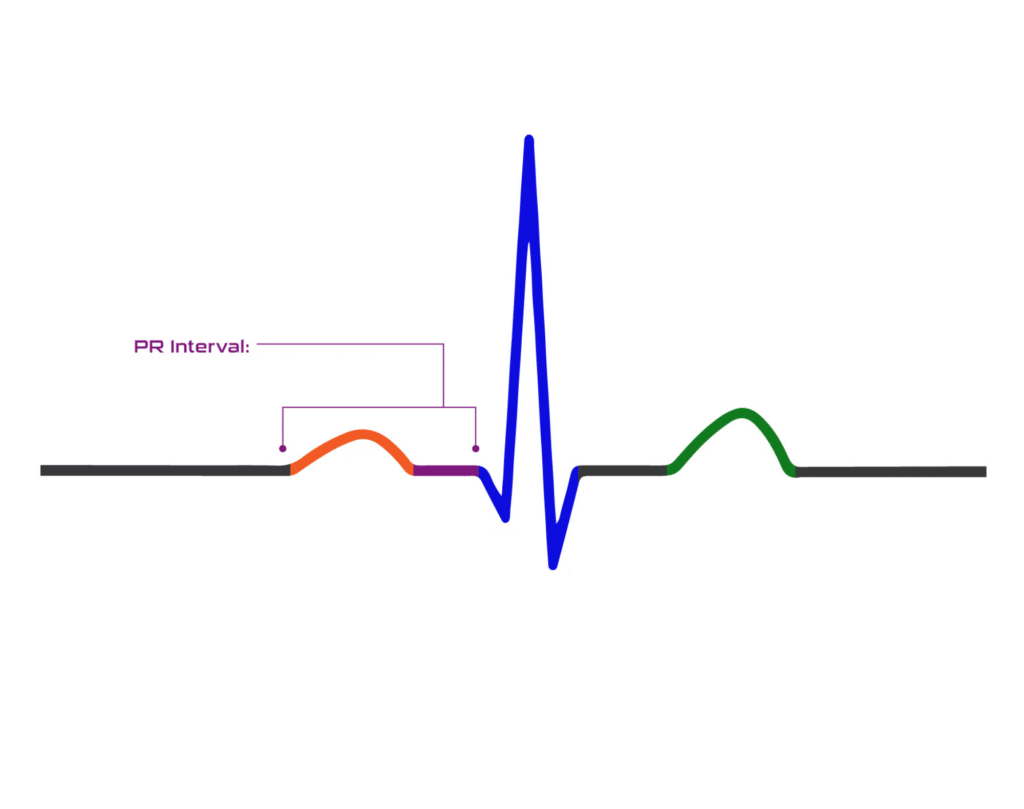
PR Interval
The PR interval begins at the P wave and ends at the start of the QRS complex. It measures the time it takes for electrical activity to travel from the upper chambers to the lower chambers of the heart.
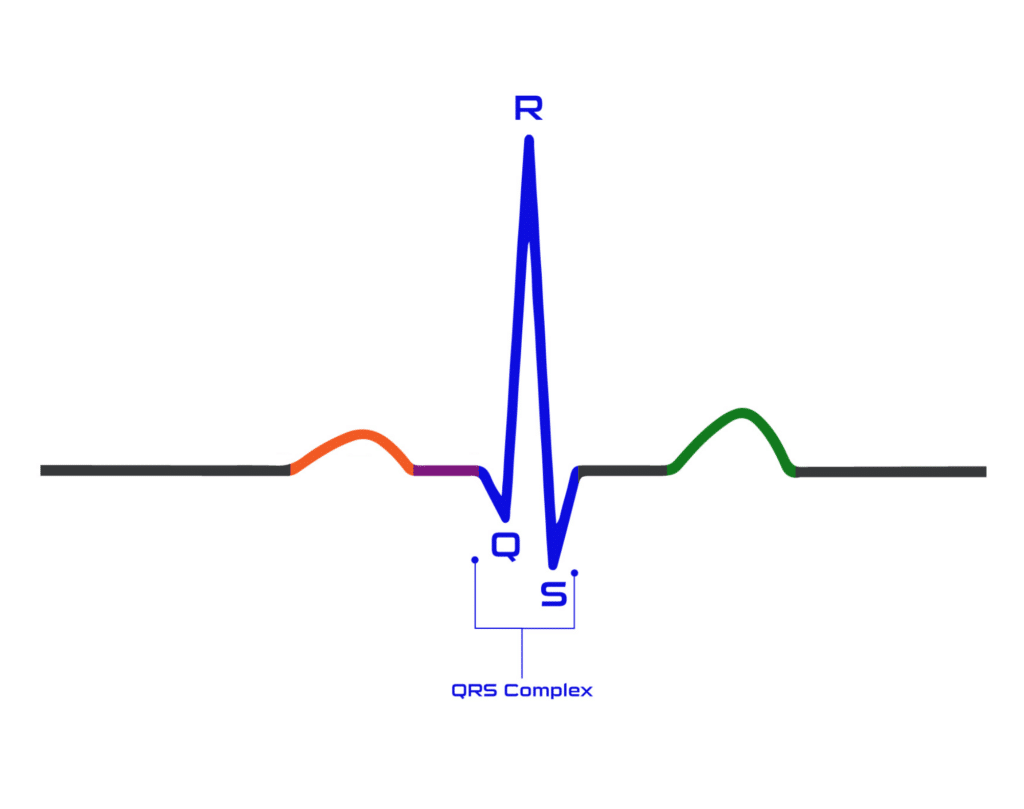
QRS Complex
The QRS complex consists of a downstroke Q wave, upstroke R wave, and downstroke S wave. Together they represent ventricular depolarization, or the time it takes for electrical activity to travel throughout the lower chambers of the heart. Not every QRS complex will show all three waves.
- Q wave: A downward deflection
- R wave: An upward deflection
- S wave: A downward deflection following the R wave
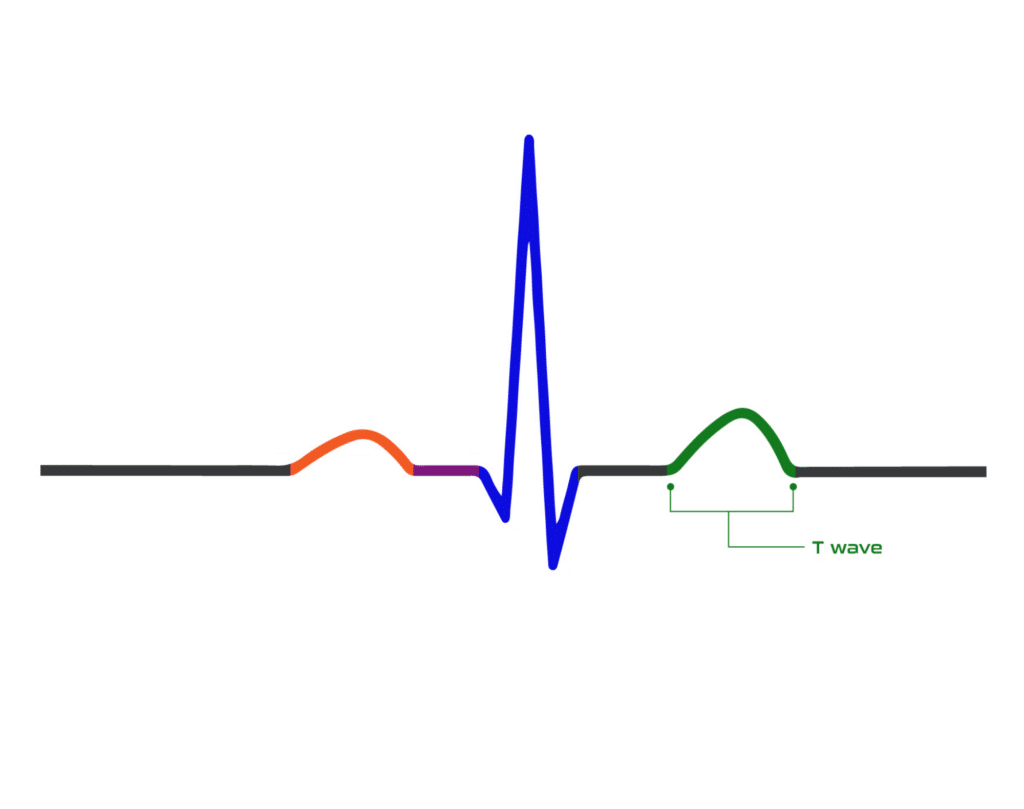
T Wave
The T wave represents ventricular repolarization, or when things go back to normal. It usually appears in an asymmetrical pattern with a peak closer to the end of the wave.
Together, these waves represent the contraction of the ventricles, and the width of the QRS complex can help determine the type of conduction in the heart. A wider QRS complex can indicate a delay in ventricular depolarization.
Why Understanding ECGs is Important
Understanding ECGs can help you recognize abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias), diagnose potential heart diseases, and monitor heart recovery after events like heart attacks. It’s an essential skill for medical professionals but can also be useful for patients who are learning more about their own heart health.
By learning the key components of an ECG—such as waves, intervals, segments, and complexes—you can become more confident in interpreting an ECG and understanding what it means for heart function.
Conclusion
Reading an ECG may seem complex at first, but with practice and knowledge of the basics, you can gain a deeper understanding of your heart’s electrical activity. Whether you’re a healthcare professional or simply someone interested in learning about the heart, understanding the core components of an ECG is a valuable skill.
If you’re learning how to interpret an ECG, be sure to keep studying the different waveforms, intervals, and complex patterns that help professionals assess heart health. Practice, along with a solid understanding of cardiac anatomy and physiology, will give you the expertise you need to become proficient in ECG interpretation.
Learn More
Don’t feel 100% confident on how to read an ECG?
Contact our team at SureFire CPR to master your heart rhythms in our online ECG class today!